By: Deepak G. Nair, MD
Occurs when your blood thickens in a clump that becomes solid, forming a clot. Nearly 300,000 first-time cases of
DVT occur in the U.S. every year, usually in the leg.
Requires prompt attention
If you develop a clot and a piece of it breaks off, it could travel to one of your lungs and make breathing difficult, or
even cause death.
Medically treatable
Most commonly treated with blood thinners.
Medium term
Can last from weeks to months.
Have specific questions? Find a vascular specialist near you.
Symptoms
May be Absent
DVT can occur without any warning signs.
Discomfort Along the Affected Vein
Swelling, pain, redness or warmth along the vein that has the clot.
Causes
DVT forms when your blood flow becomes very slow.
Some specific causes of DVT include:
- Inactivity, such as after a major operation or during a flight.
- Damage to a vein can cause a clot to form – especially damage from a catheter, like those used in dialysis , or
- from a PICC line.
- Cancer and certain other diseases and genetic conditions, called hypercoagulable states, that cause your blood
- to clot more easily.
- Medications, especially hormones.
Diagnosis
See a Vascular Surgeon
You will be asked questions about symptoms and medical history, including questions about family members. The
vascular surgeon will also perform a physical exam.
Tests May Be Recommended
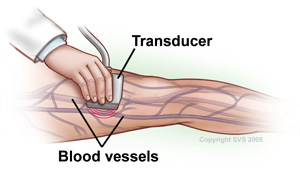
A blood test known as a D-dimer
A duplex ultrasound test
Treatments
DVT is usually treated with medication.
Blood Thinners
Also known as anticoagulants, are the most common medicines used for treating DVT. They prevent blood clots from
getting larger by decreasing your blood’s ability to clot. Over time, your body works with the blood thinners to decrease
the size and consistency of the clot. Blood thinners can be taken as a pill, as an injection or intravenously (through an
IV). Blood thinners can increase your chance of bleeding, so careful follow-up with your vascular surgeon is
necessary.
Thrombolytic Therapy
Sometimes used to quickly dissolve a blood clot, especially if the clot is large and causing severe symptoms. This
treatment brings a much higher risk of bleeding than blood thinners, so it is not used unless truly necessary.
An IVC Filter
Placed inside the inferior vena cava, one of the largest veins in the body, may be an option. The filter does not stop a
blood clot from forming, but can prevent a large clot from entering your lungs.
Staying Healthy
Maintain good overall health to decrease your risk of DVT.
- Stay physically active. This is very important following surgery and during long trips.
Maintain a normal weight.
Seek treatment quickly for any medical problem, such as infection or cancer. - If you have a blood clot now or ever had one, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits of staying on blood
- thinners with your vascular surgeon.

